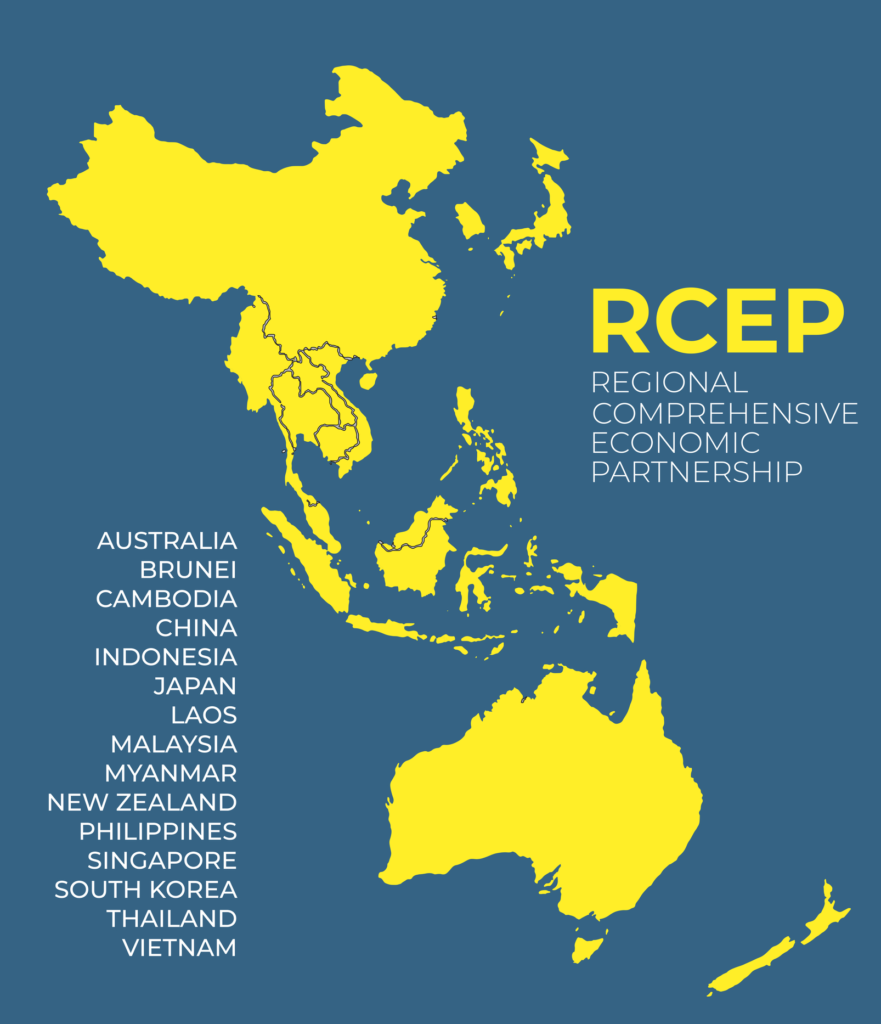
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), hailed as the world’s largest trading agreement, emerged as a transformative force in the global economic arena. Originating from negotiations dating back to the ASEAN Cambodia summit in 2012, RCEP aimed to facilitate the seamless flow of products and services across its diverse member countries. This article provides a comprehensive overview of RCEP, covering its formation, objectives, significance, and the intricate dynamics surrounding its implementation.
Formation and Objectives:
Established as a result of negotiations initiated in 2012, RCEP brought together 10 member countries of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and six nations with pre-existing free trade agreements (FTA) with the ASEAN bloc. These FTAs encompassed India, Australia, China, South Korea, Japan, and New Zealand. The core objective of RCEP was to enhance regional trade by simplifying the availability of products and services across member countries, promoting economic growth and stability.
Alternative to Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP):
RCEP emerged as a significant alternative to the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), a proposed trade agreement that excluded China and India. The withdrawal of the United States from the TPP bolstered the prospects of success for RCEP, positioning it as a crucial player in shaping the economic dynamics of the Asia-Pacific region.
Key Features and Achievements:
RCEP aimed to achieve a high level of tariff liberalization by building upon existing levels of liberalization among participating countries. Signed on November 15, 2020, during a virtual ASEAN summit hosted by Vietnam, the agreement was set to become operational once ratified by at least six ASEAN and three non-ASEAN signatories. The threshold for entry into force was met on January 1, 2022, with Australia and New Zealand being the latest members to ratify the agreement.
The agreement is expected to eliminate approximately 90% of tariffs on imports between signatories within 20 years of implementation. Additionally, RCEP establishes common rules for e-commerce, trade, and intellectual property, promoting a harmonized economic environment. Unified rules of origin facilitate international supply chains, reducing export costs and enhancing efficiency throughout the bloc.
India’s Opt-Out and Concerns:
India decided not to join RCEP in November 2019, citing concerns related to competition with China and the potential inundation of Chinese goods in Indian markets. Prime Minister Narendra Modi highlighted that the agreement did not adequately address India’s concerns, emphasizing the need for a more balanced and mutually beneficial arrangement.
Future Prospects and Global Impact:
RCEP’s entry into force marks a significant milestone in reshaping the economic landscape of the Asia-Pacific region. With the potential to eliminate barriers to trade and establish a cohesive economic bloc, RCEP is expected to surpass both the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement and the European Union in scale. Analysts initially predicted that the agreement would stimulate economic growth amidst the COVID-19 pandemic and contribute to shifting the global economic center of gravity towards Asia, impacting the influence of the United States in economic and political affairs.
Conclusion:
The implementation of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership signifies a new era of economic collaboration and integration in the Asia-Pacific region. As the world’s largest trading agreement, RCEP’s impact extends beyond its member countries, influencing global trade dynamics and redefining the balance of economic power. The evolving narrative of RCEP underscores the complexities and opportunities inherent in forging multinational agreements that seek to foster economic prosperity and stability.